SuperB
The SuperB flavour Factory, a major international research centre for fundamental and applied physics will be built on the campus of the University of Rome "Tor Vergata". The project proposed by the INFN is first on the list of the 14 flagship projects of the National Research Plan of the Italian Ministry for Education, Universities and Research (MIUR).
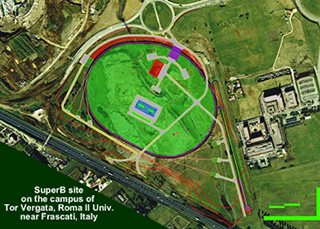 The project involves the construction of a large electron-positron collider located in an area of approximately 30 hectares on the campus of the University of Rome "Tor Vergata" and closely linked to the INFN Frascati National Laboratories, located nearby.
The project involves the construction of a large electron-positron collider located in an area of approximately 30 hectares on the campus of the University of Rome "Tor Vergata" and closely linked to the INFN Frascati National Laboratories, located nearby.
The physicists' objective is to cast light on some of the great questions of contemporary physics: for example on the mechanisms which led to the disappearance of antimatter shortly after the Big Bang at the dawn of the history of our Universe, or on the forces which hold the fundamental components of matter together. The SuperB research programme can be seen as complementary to that of CERN's Large Hadron Collider (LHC), since the two accelerators deal with two different frontiers of experimental subnuclear physics: intensity and energy. SuperB will concentrate on increasing the rate of the particle beam collisions in order to observe extremely rare physical phenomena, while the LHC, which has enormously increased the energy at which proton collisions take place, is probing new physics directly by producing potentially new particles. The leap forward in luminosity (the rate of collisions) of SuperB is based on ideas developed in Italy and experimented in 2008-2009 at the INFN Frascati National Laboratories, using the DAFNE collider.
Moreover, the SuperB infrastructure will also provide new technologies and advanced experimental instruments for research in the domains of solid state physics, biology, nanotechnologies and biomedicine.

