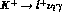 has the
structure
has the
structure
The matrix element for 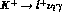 has the
structure
has the
structure
with
Here, 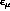 denotes the polarization vector of the photon with
denotes the polarization vector of the photon with
 , whereas A,
V stand for two Lorentz
invariant amplitudes which occur in the general decomposition of the
tensors
, whereas A,
V stand for two Lorentz
invariant amplitudes which occur in the general decomposition of the
tensors
The form factor A 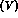 is related to the matrix element of
the axial (vector)
current in (1.4).
In appendix C we display the general
decomposition of
is related to the matrix element of
the axial (vector)
current in (1.4).
In appendix C we display the general
decomposition of 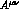 ,
,
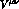 for
for  and provide also the link with the notation
used by the PDG [3] and in [4,5].
and provide also the link with the notation
used by the PDG [3] and in [4,5].
The term proportional to 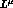 in (1.2) does not contain
unknown quantities -- it
is determined by the amplitude of the nonradiative decay
in (1.2) does not contain
unknown quantities -- it
is determined by the amplitude of the nonradiative decay 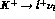 . This part of the amplitude is usually referred to as ``inner
Bremsstrahlung (IB) contribution", whereas the term proportional to
. This part of the amplitude is usually referred to as ``inner
Bremsstrahlung (IB) contribution", whereas the term proportional to 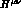 is called ``structure dependent (SD) part" .
is called ``structure dependent (SD) part" .
The form factors are analytic functions in the complex 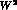 -plane cut
along the positive real axis. The cut starts at
-plane cut
along the positive real axis. The cut starts at 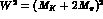 for
A (at
for
A (at 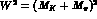 for V). In our phase convention, A and
V are real in the physical region of
for V). In our phase convention, A and
V are real in the physical region of 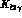 decays,
decays,
The kinematics of (spin averaged) 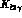 decays needs two
variables, for which we choose the conventional quantities
decays needs two
variables, for which we choose the conventional quantities
In the K rest frame, the variable x (y) is proportional to the photon (charged lepton) energy,
and the angle 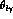 between the photon and the charged lepton is
related to x and y by
between the photon and the charged lepton is
related to x and y by
In terms of these quantities, one has
We write the physical region for x and y as

or, equivalently, as
where