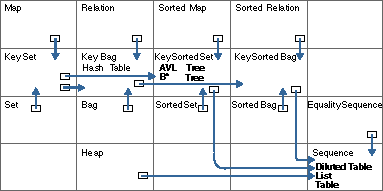
The figure below lists the basic and based-on implementations provided by the Collection Classes. The upper left corner of each cell contains the name of the (abstract) collection class; basic implementations are written in smaller letters in bold face, while based-on implementations are described by arrows starting from the class that they implement and ending in the (abstract) class on which they are based. An implementation choice for a given class must use either a basic implementation for this class or follow a based-on implementation path that ultimately leads to a basic implementation.

Take the example of the Set abstraction. The Set is not implemented directly. (You can tell this from the figure because no implementation variant name appears in bold in the box containing Set.) To determine the possible implementation variants for Set, follow the arrows out of the Set box:
A Set can therefore be implemented using any of the six implementation variants cited in bold face above.
Implementation variants are provided for each flat collection. D identifies the default implementations; I identifies implementation variants. If the space is blank, the feature is not supported.
| Implementation Variant | Implementation Variants | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bag | Sorted Bag | Key Bag | Key Sorted Bag | Set | Sorted Set | Key Set | Key Sorted Set | Map | Sorted Map | Relation | Sorted Relation | Sequence | Equality Sequence | Heap | |
| AVL Tree | D | D | D | D | D | D | |||||||||
| B* Tree | I | I | I | I | I | I | |||||||||
| Hash Table | I | D | I | I | I | D | |||||||||
| List | D | D | I | D | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | D | D | D | D |
| Table | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I |
| Diluted Table | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I | I |
![]()
Introduction
to the Collection Classes
Collection
Class Hierarchy
Collection Characteristics
Flat
Collections
Trees
![]()
Class Template Naming
Conventions
Choosing One of the
Provided Implementation Variants
Taking Advantage of
the Abstract Class Hierarchy
Instantiating the
Collection Classes
Troubleshooting
Problems while Using the Collection Class Library