


Next: 2 Time evolution
Up: Chapter 1 Section 4
Previous: Chapter 1 Section 4
The 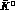
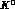 state produced in the decay of the
state produced in the decay of the  resonance is odd under charge conjugation and is therefore an antisymmetric
resonance is odd under charge conjugation and is therefore an antisymmetric
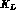
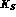 state. This characteristic makes a
state. This characteristic makes a  factory very
suitable to study CP violation and to test CPT symmetry in K meson
decays [1,2].
factory very
suitable to study CP violation and to test CPT symmetry in K meson
decays [1,2].
For a long time it has been stressed that
the presence in the same detector of 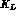 and
and 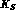 beams,
produced without regeneration and thus with the
relative fluxes perfectly known, will allow a very clean determination of the
ratio
beams,
produced without regeneration and thus with the
relative fluxes perfectly known, will allow a very clean determination of the
ratio 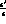 [3].
A non-zero value for
[3].
A non-zero value for 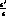 is an unambiguous signal of
the existence of direct CP violation, which is naturally expected in the
Standard Model. The present experimental situation is:
is an unambiguous signal of
the existence of direct CP violation, which is naturally expected in the
Standard Model. The present experimental situation is:
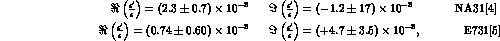
still consistent with 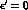 .
The theoretical calculation of
.
The theoretical calculation of 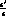 in the Standard Model
is strongly affected by QCD corrections and, for large values
of the top mass, large cancellations are expected [6].
The present estimate is
in the Standard Model
is strongly affected by QCD corrections and, for large values
of the top mass, large cancellations are expected [6].
The present estimate is 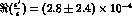 ,
[7] thus a fundamental goal of DA
,
[7] thus a fundamental goal of DA NE
is certainly to reach the sensitivity of
NE
is certainly to reach the sensitivity of 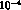 in the measurement
of this ratio. Independent information about direct CP violation
could be obtained also by charge asymmetries in
in the measurement
of this ratio. Independent information about direct CP violation
could be obtained also by charge asymmetries in
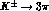 [8]
and
[8]
and 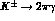 [9] decays.
[9] decays.
Beyond the study of direct CP violation,
the presence of a pure 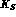 beam will allow
the observation at DA
beam will allow
the observation at DA NE of some suppressed
NE of some suppressed 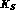 decays,
such as the semileptonic and the three-pion ones.
The theoretical predictions for semileptonic
decays are not strongly affected by QCD corrections and, as
we will discuss later, the measurement of the semileptonic rates and
charge asymmetries in
decays,
such as the semileptonic and the three-pion ones.
The theoretical predictions for semileptonic
decays are not strongly affected by QCD corrections and, as
we will discuss later, the measurement of the semileptonic rates and
charge asymmetries in 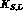 decays can give many interesting
tests of CPT and of the
decays can give many interesting
tests of CPT and of the 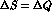 rule. Moreover, due to the
coherence of the initial state, T and CPT symmetries can be
directly tested in events with two leptons in the final state
[10,11].
rule. Moreover, due to the
coherence of the initial state, T and CPT symmetries can be
directly tested in events with two leptons in the final state
[10,11].
Some time ago it was pointed out that the radiative decay
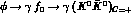 could have a non-negligible branching ratio [12] and therefore
a dangerous background, namely a
could have a non-negligible branching ratio [12] and therefore
a dangerous background, namely a 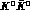 component even
under charge conjugation, could be present.
New determinations of the
component even
under charge conjugation, could be present.
New determinations of the 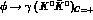 branching ratio [13] turn
out to be much smaller, then, as we will show, the inclusion of
the C-even background does not sensibly affect
the measurements of
branching ratio [13] turn
out to be much smaller, then, as we will show, the inclusion of
the C-even background does not sensibly affect
the measurements of 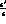 and
and 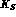 suppressed decays.
suppressed decays.
It has been suggested that quantum mechanics
violations may be generated by non-local theories
at the Planck scale [14]. As a consequence
CP- and CPT-violating effects of non quantum-mechanical origin
could be induced [15,16]. In [16]
it was proposed to investigate such effects in quantum correlated
particle systems, such as the 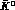
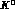 system.
The coherence of the
system.
The coherence of the  -factory
initial state will help in disentangling
these effects, and quite stringent bounds could be obtained for
the quantum mechanics violating parameters [17,18].
It is worth while to note that the quantum mechanics violation induces
a loss of the initial state coherence which can somehow
simulate the effect of a C-even background.
-factory
initial state will help in disentangling
these effects, and quite stringent bounds could be obtained for
the quantum mechanics violating parameters [17,18].
It is worth while to note that the quantum mechanics violation induces
a loss of the initial state coherence which can somehow
simulate the effect of a C-even background.
The plan of the paper is the following: in section 2 we recall the
time evolution of the initial state. In section 3 we report its implications
on the determination of real and imaginary parts of 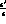 .
In section 4 the
semileptonic decays, with possible direct tests of
T and CPT symmetry, are discussed. Sections 5 and 6 are devoted, respectively,
to
.
In section 4 the
semileptonic decays, with possible direct tests of
T and CPT symmetry, are discussed. Sections 5 and 6 are devoted, respectively,
to 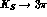 and
and 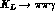 decays.
In section 7 we
study the effect of the C-even background. In
section 8 we discuss the implications of
possible quantum mechanics violations. Finally, in the appendix,
the relation between time and distance measurements are discussed.
decays.
In section 7 we
study the effect of the C-even background. In
section 8 we discuss the implications of
possible quantum mechanics violations. Finally, in the appendix,
the relation between time and distance measurements are discussed.



Next: 2 Time evolution
Up: Chapter 1 Section 4
Previous: Chapter 1 Section 4
Carlos E.Piedrafita
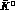
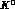 state produced in the decay of the
state produced in the decay of the  resonance is odd under charge conjugation and is therefore an antisymmetric
resonance is odd under charge conjugation and is therefore an antisymmetric
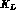
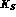 state. This characteristic makes a
state. This characteristic makes a  factory very
suitable to study CP violation and to test CPT symmetry in K meson
decays [1,2].
factory very
suitable to study CP violation and to test CPT symmetry in K meson
decays [1,2].
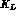 and
and 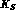 beams,
produced without regeneration and thus with the
relative fluxes perfectly known, will allow a very clean determination of the
ratio
beams,
produced without regeneration and thus with the
relative fluxes perfectly known, will allow a very clean determination of the
ratio 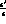 [
[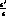 is an unambiguous signal of
the existence of direct CP violation, which is naturally expected in the
Standard Model. The present experimental situation is:
is an unambiguous signal of
the existence of direct CP violation, which is naturally expected in the
Standard Model. The present experimental situation is:
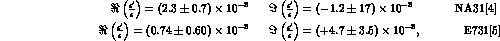
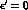 .
The theoretical calculation of
.
The theoretical calculation of 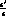 in the Standard Model
is strongly affected by QCD corrections and, for large values
of the top mass, large cancellations are expected [
in the Standard Model
is strongly affected by QCD corrections and, for large values
of the top mass, large cancellations are expected [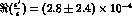 ,
[
,
[ NE
is certainly to reach the sensitivity of
NE
is certainly to reach the sensitivity of 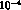 in the measurement
of this ratio. Independent information about direct CP violation
could be obtained also by charge asymmetries in
in the measurement
of this ratio. Independent information about direct CP violation
could be obtained also by charge asymmetries in
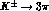 [
[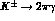 [
[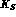 beam will allow
the observation at DA
beam will allow
the observation at DA NE of some suppressed
NE of some suppressed 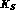 decays,
such as the semileptonic and the three-pion ones.
The theoretical predictions for semileptonic
decays are not strongly affected by QCD corrections and, as
we will discuss later, the measurement of the semileptonic rates and
charge asymmetries in
decays,
such as the semileptonic and the three-pion ones.
The theoretical predictions for semileptonic
decays are not strongly affected by QCD corrections and, as
we will discuss later, the measurement of the semileptonic rates and
charge asymmetries in 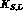 decays can give many interesting
tests of CPT and of the
decays can give many interesting
tests of CPT and of the 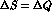 rule. Moreover, due to the
coherence of the initial state, T and CPT symmetries can be
directly tested in events with two leptons in the final state
[
rule. Moreover, due to the
coherence of the initial state, T and CPT symmetries can be
directly tested in events with two leptons in the final state
[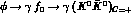 could have a non-negligible branching ratio [
could have a non-negligible branching ratio [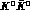 component even
under charge conjugation, could be present.
New determinations of the
component even
under charge conjugation, could be present.
New determinations of the 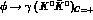 branching ratio [
branching ratio [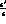 and
and 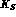 suppressed decays.
suppressed decays.
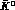
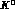 system.
The coherence of the
system.
The coherence of the  -factory
initial state will help in disentangling
these effects, and quite stringent bounds could be obtained for
the quantum mechanics violating parameters [
-factory
initial state will help in disentangling
these effects, and quite stringent bounds could be obtained for
the quantum mechanics violating parameters [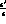 .
In section 4 the
semileptonic decays, with possible direct tests of
T and CPT symmetry, are discussed. Sections 5 and 6 are devoted, respectively,
to
.
In section 4 the
semileptonic decays, with possible direct tests of
T and CPT symmetry, are discussed. Sections 5 and 6 are devoted, respectively,
to 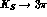 and
and 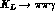 decays.
In section 7 we
study the effect of the C-even background. In
section 8 we discuss the implications of
possible quantum mechanics violations. Finally, in the appendix,
the relation between time and distance measurements are discussed.
decays.
In section 7 we
study the effect of the C-even background. In
section 8 we discuss the implications of
possible quantum mechanics violations. Finally, in the appendix,
the relation between time and distance measurements are discussed.